First 'porous liquid' invented
16. 11. 2015 | Phys.org | www.phys.org
Researchers in the School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering at Queen's, along with colleagues at the University of Liverpool and other, international partners, have invented the new liquid and found that it can dissolve unusually large amounts of gas, which are absorbed into the “holes” in the liquid. The results of their research are published today in the journal Nature.
The three-year research project could pave the way for many more efficient and greener chemical processes, including ultimately the procedure known as carbon capture - trapping carbon dioxide from major sources, for example a fossil-fuel power plant, and storing it to prevent its entry into the atmosphere.
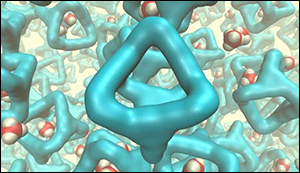
Professor Stuart James of Queen's School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering said: “Materials which contain permanent holes, or pores, are technologically important. They are used for manufacturing a range of products from plastic bottles to petrol. However, until recently, these porous materials have been solids. What we have done is to design a special liquid from the 'bottom-up' - we designed the shapes of the molecules which make up the liquid so that the liquid could not fill up all the space. Because of the empty holes we then had in the liquid, we found that it was able to dissolve unusually large amounts of gas. These first experiments are what is needed to understand this new type of material, and the results point to interesting long-term applications which rely on dissolution of gases.”
Read more at Phys.org
Image Credit: Queen's University Belfast
-jk-




